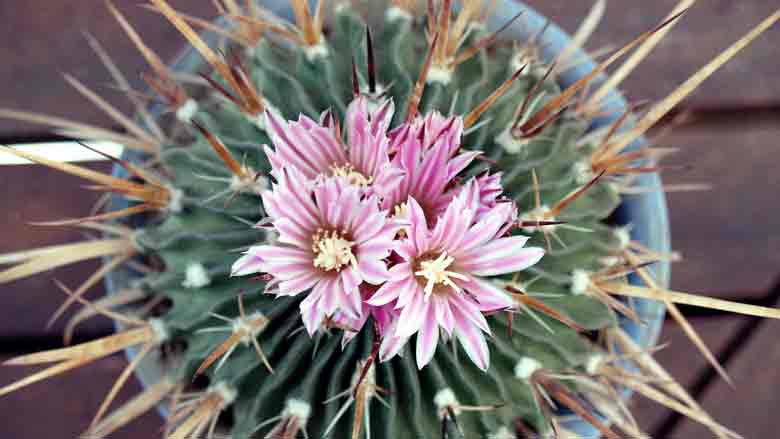
Do you know how cacti reproduce? It’s a fascinating process that not many people know about.
Cacti can reproduce either sexually or asexually, and the way they do it depends on the species.
This article will discuss how cactus reproduction works and some of the different methods that cacti use to propagate.
If you’re interested in learning more about cactus reproduction, keep reading!
How Does a Cactus Reproduce?
There are two ways that cacti can reproduce.
One way is through sexual reproduction, where the plant produces flowers that bees or other insects pollinate.
After the flowers are pollinated, the fruit of the cactus will develop and eventually split open to release the seeds.
Another way cacti can reproduce is through a process called asexual reproduction.
This is where the cactus will produce a new plant from a cutting, grafting, or division.
Growers often use asexual reproduction to create new plants that are clones of the parent plant.
Both reproduction methods are effective ways for cacti to spread and create new plants.
By understanding how cacti reproduce, you can better care for these unique plants.
How Do Cacti Reproduce Sexually?
Cacti, like most succulents, reproduce sexually and asexually depending on the variety.
Cacti are flowering plants, and, like all flowering plants, they reproduce with seeds.
To reproduce sexually, cacti need two things: pollen and a stigma. The pollen is produced in the flower’s anthers, and the stigma is on the tip of the pistil.
When the pollen from one cactus meets up with the stigma of another cactus, fertilization occurs, and seeds are formed.
Fertilization happens when insects or other animals pollinate the cactus flowers.
The flowers produce fruit that contains seeds. Once the fruit matures, it dries out and splits open, releasing the cactus seeds.
Cacti rely on a wide range of pollinators, including simple techniques like wind transfer and more complex symbiotic relationships with birds and insects like bees, butterflies, moths, and beetles.
Flowers have a specific smell and color that attract pollinators.
Pollen adheres to the pollinator’s body as it consumes the nectar from the cactus flower and is then carried from the stamens to the pistil by pollinators.
However, through self-pollination, most cactus reproduce sexually without any help from outside sources.
Self-pollination occurs when the pollen from one plant fertilizes the ovules of the same cactus.
However, cross-pollination between different cacti produces healthier plants with more genetic diversity.
Sexual reproduction in cacti generally occurs between late spring and early summer.
During this time, cacti produce flowers that insects or other animals pollinate.
After pollination, the flowers produce fruits that contain seeds. When the cactus fruit matures, it falls to the ground, and the seeds germinate, creating new cacti.
How Do Cacti Reproduce Asexually?
Asexual reproduction refers to the process of creating new plants without the use of seeds.
Cacti can reproduce asexually through a process called vegetative propagation.
Vegetative propagation is the process of a new cactus growing from a part of an existing cactus.
The benefits of asexual reproduction are that it is faster than sexual reproduction, and it produces genetically identical plants to the parent plant.
There are several ways that cacti can reproduce asexually, including:
- Offsets
- Cuttings
- Grafting
- Division
Propagating Cactus Plants from Offsets
Offsets are small plants that grow at the base of the mother cactus.
They are clones of the mother plant and can be separated from the parent plant and grown into new plants.
To propagate cacti from offsets, cut off the offset with a sharp knife or shears and place it in a pot filled with a cactus mix.
Water the offset and place it in a warm, sunny spot. The offset will root and grow into a new plant.
Propagating Cactus Plants from Cuttings
Cuttings are one of the easiest and most popular ways to propagate cactus plants.
A cactus cutting is simply a piece of the stem or main body of the plant that you cut off and then grow in its own pot.
To take a cactus cutting, use a sharp knife or pair of scissors to remove a section of the stem.
The stem cutting should be at least two inches long and include one or more joints (the parts of the stem where it bends).
Make sure to cut the stem cleanly without damaging the cactus tissue.
Once you have your cutting, allow it to callus over for a day or two. This is when the cut end of the stem dries out and forms a protective barrier.
Once the cutting has callused, you can plant it in potting soil.
Be sure to use a pot with drainage holes and cactus potting mix, as regular potting soil is too dense and will not drain properly.
Place the cutting in the soil so that the callused end is buried and the rest of the stem is above ground.
Water the soil lightly, just enough to moisten it. Place the pot in a bright spot, out of direct sunlight.
Cactus cuttings can take a few weeks to several months to root and start growing.
Be patient and don’t water too often, as this can cause the cutting to rot.
Once the plant starts to grow, you can treat it like a regular cactus plant!
Grafting Cactus Plants
Grafting is the process of joining two different cactus plants together to create a new plant.
The plants used for grafting must be similar in size and shape and must have the same rooting requirements.
To graft two cacti plants, cut off the top of one plant (the part that will become the new head) and cut a slice out of the bottom of the other plant.
Make sure to cut cleanly and avoid damaging the cactus tissue.
The two plants should be matched up to match the slices together like puzzle pieces, then use grafting tape or wax to hold them in place.
Once the plants are grafted together, they need to be placed in a bright spot and given time to heal.
After a few weeks, the two plants will have grown together and can be treated as one plant.
Propagating Cactus Plants from Division
Cacti can also be propagated by division, which is the process of splitting a cactus plant into two or more plants.
To propagate cacti from division, you will need to remove the cactus from its pot and then use a sharp knife to divide it into two or more pieces.
Each piece should have its own root system.
Once you have divided the cactus, replant each piece in its own pot filled with a cactus mix.
Water the soil and place the pots in a warm, sunny spot.
The cacti will start to grow and should be treated as regular cactus plants.
How Often Does a Cactus Reproduce?
Cacti can reproduce either sexually or asexually.
Most cactus plants will reproduce sexually by producing flowers and seeds.
The frequency of cactus reproduction depends on the species. Some cacti may only reproduce once a year, while others reproduce several times.
In general, Cactus plants bloom once a year and reproduce sexually.
Depending on the cactus species, the flowers will usually appear in the late winter or early spring.
After the flowers have been pollinated, the cactus will produce small green fruits that contain seeds.
Cacti also grow offsets, or “baby cacti”, which are tiny replicas of the parent plant that can be used to propagate new plants.
Offsets can be produced asexually through vegetative reproduction. This is when the cactus plant produces offsets without having flowers or seeds.
Most cacti will produce offsets at some point in their lifetime, although the frequency varies depending on the species.
Some cacti may only produce a few offsets every few years, while others produce several offsets every month.
On the other hand, propagating cacti through the methods mentioned above is faster and easier than sexual propagation.
It is also unnecessary to wait for the cactus flower to bloom to propagate new plants.
These methods are relatively easy and can be done with minimal effort. As long as you have a healthy cactus plant, you can produce new plants when needed.
So, how often does a cactus reproduce?
It depends on the species and the method of propagation. Some cacti may only reproduce once a year, while others reproduce several times. It all depends on the plant!
How Fast Does a Cactus Reproduce?
The speed of cactus reproduction also depends on the species and the propagation method.
If a cactus reproduces sexually, it will take a few weeks to a few months for the flowers to be pollinated and the fruits to mature.
On the other hand, if a cactus is reproducing vegetatively, it will take anywhere from a few days to a few weeks for the offsets to be produced.
So, how fast does a cactus reproduce? It depends on the species and the method of propagation!
For example, offsets can be produced relatively quickly, usually within a few weeks or months. However, it may take years for a cactus to produce seeds.
Final Thoughts
Growing cactus plants from seeds can be a rewarding experience, but it does require some patience.
Some cacti will flower and produce fruit almost immediately after being transplanted into the garden, while others may take several years to reach flowering size.
When grown from seed, most cactus plants will eventually reach maturity and reproduce on their own.
However, if you want to speed up the process, you can help your cactus by providing it with the ideal growing conditions.
Also, if you don’t want to wait for your cactus to flower and fruit naturally, you can propagate them by taking cuttings from existing plants.
Cacti can be propagated with several methods, but the most common and easiest way is to cut from an existing plant’s stem.
Cacti are unique plants, and they make a great addition to any garden.
With a little bit of knowledge and some basic care, you can enjoy these fascinating plants for many years to come.