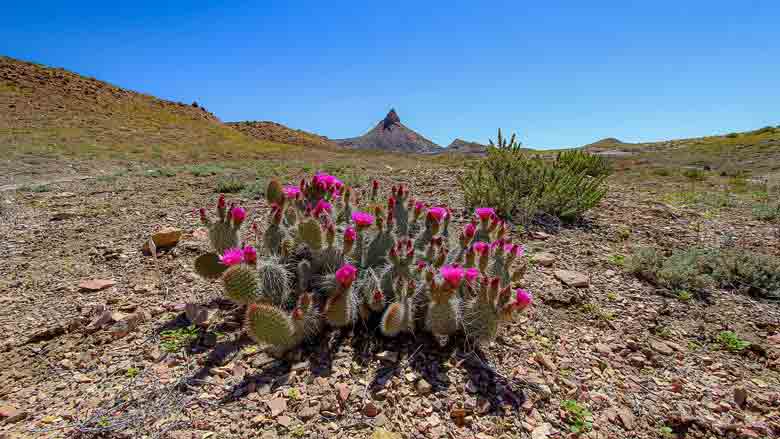
There are many different types of cacti, and they can be found in a variety of habitats around the world.
One of the most interesting places to find cacti is in the desert.
But how do cacti survive in the desert?
It is a harsh and unforgiving environment, yet these plants manage to thrive.
How do they do it?
Cacti have some unique adaptations that allow them to thrive in this extreme environment.
This article will discuss some of these adaptations and how they help cacti survive in the desert!
How Do Cacti Adapt to the Desert?
Cactus plants are known for their ability to thrive in hot, dry habitats.
The desert is one of the harshest environments on Earth, yet cacti have adapted to survive in this hostile environment.
Cacti, like all plants, have developed unique strategies to cope with their specific set of environmental conditions.
In the case of the desert, it is the extreme heat and lack of water that present the biggest challenges.
This extreme environment has led to some interesting adaptations in cacti.
Below are some fascinating ways that cacti have adapted to survive in the desert.
What Adaptations Does a Cactus Have To Survive in the Desert?
Cactus plants have several adaptations that allow them to survive in the desert.
These characteristics allow cacti to conserve water, reduce heat stress, and photosynthesize efficiently.
Some of the most essential adaptations are listed below.
1. Thorns and Spines
One of the most obvious adaptations cacti have for desert life is their thorns and spines, which, contrary to a common misconception, are not typically poisonous.
Cacti have developed spines instead of leaves to minimize water loss since leaves increase the plant’s surface area and require more water to stay hydrated.
The spines also protect cacti from being eaten by animals and reduce heat stress to keep the cactus cooler by deflecting sunlight.
They also help the plant collect moisture from the air by trapping humidity and directing it towards its roots.
While the thorns and spines of cacti may seem like a deterrent, they are an important adaptation for desert life.
These structures help the plant to conserve water and protect itself from extreme conditions.
2. Shallow Root System
Another adaptation that helps cacti survive in the desert is their shallow root system.
This shallow root system allows the plant to quickly absorb any rainfall before it evaporates.
The roots also spread outwards, which helps the plant stabilize itself in the sand and prevents it from being blown over by strong winds.
Cacti also have many root hairs, which increases the surface area that can absorb water.
These adaptations allow cacti to quickly take advantage of any rainfall and survive in an environment where water is scarce.
3. Waxy Coating
Cacti also have a waxy coating that helps to reduce water loss.
Cactus plants store water in their stems, which helps keep the plant hydrated during periods of drought.
This water-storage ability is one of the most important adaptations for desert life.
This waxy coating seals in moisture and prevents the plant from losing water through its leaves or stem.
It also helps to reduce the amount of sunlight that is absorbed, which reduces heat stress and prevents the plant from overheating.
The waxy coating is an important adaptation that helps cacti survive in the desert by reducing water loss and heat stress.
4. Stomata Closure
Cactus plants need to conserve water in the desert by shutting down photosynthesis during the day and only opening their stomata at night.
The stomata are tiny pores on the leaves that allow the plant to absorb carbon dioxide and release water vapor.
To conserve water, cacti have developed the ability to close their stomata and prevent water loss through transpiration.
Transpiration is the process by which water vapor escapes from the leaves of a plant.
Cacti can prevent water loss and reduce the amount of water they need to survive by closing their stomata during the day.
At night, when it is cooler, the cactus will open its stomata to take in carbon dioxide for photosynthesis.
This adaptation allows cacti to survive in the desert by reducing water loss through transpiration.
5. Water-Storage Cells
Cacti have adapted to the desert by developing water storage cells in their stems.
These water-storage cells help the plant store water and stay hydrated during periods of drought.
The cells can store large amounts of water, which helps the cactus survive in an environment where water is scarce.
The water-storage cells also help keep the plant upright, as they are heavier than the plant’s other tissues.
This adaptation allows cacti to survive in the desert by storing water and staying hydrated during periods of drought.
6. Thick and Expandable Stems
The thick, fleshy, and expandable stems of cacti are another adaptation that helps them survive in the desert.
The thick stems help store water and keep the plant hydrated during periods of drought.
The cactus stems can also expand and contract, which helps the plant regulate its water intake.
This adaptation allows cacti to survive in the desert by storing water and regulating their water intake.
This way, cacti can expand their stems to take in more water when it rains.
The fleshy stems of cacti can hold up to 4200 pounds of water.
The thick and expandable cactus stems also help insulate the plant from extreme heat, as they can store large amounts of water and act as a thermal buffer.
This adaptation allows cacti to survive in the desert by storing water and keeping the plant hydrated during periods of drought and by insulating the plant from extreme heat.
7. Spherical Shape
The spherical shape of cacti is another adaptation that helps them survive in the desert.
The stems of desert cacti are thick and often round, columnar, cylindrical, or barrel-shaped in form.
The spherical shape helps the plant minimize the surface area exposed to the sun, reducing water loss through evaporation.
The round shape also helps the plant deflect heat, as the rounded surfaces reflect more sunlight than flat surfaces.
This minimizes heat stress and prevents the plant from overheating.
The spherical shape is an important adaptation that helps cacti survive in the desert by reducing water loss and heat stress.
8. Short Growing Season
Cactus plants have a long-dormant period followed by a short growing season. In the Mojave and Sonoran deserts, cacti may only grow for two to three months out of the year.
This is because these desert regions experience extremely high temperatures during the summer months, which prevent plant growth.
The short growing season imposes a great challenge for cacti, as they must make the most of their limited time to produce flowers and fruit.
To cope with the short growing season, cacti have evolved several strategies.
For example, some cactus species only flower for a few days each year, while others delay flowering until after the hottest part of the summer has passed.
Additionally, many cactus plants produce large amounts of fruit compared to other desert plants.
This ensures that even if some of the fruit is eaten by animals or lost to the harsh conditions, enough will survive to ensure the continuation of the species.
The short growing season is another challenge that cacti have evolved to overcome to survive in the desert.
9. Long-Dormant Period
Cacti have a long-dormant period that helps them to survive in the desert.
During the long-dormant period, cactus plants do not grow, and they do not take up water.
This allows the plant to save its limited water resources during the short growing season.
The long-dormant period also helps the plant to survive during the hot, dry summer months.
This adaptation allows cacti to survive in the desert by going into a dormant state during the hot, dry summer months.
10. Large Flowers and Colorful Fruits
Cacti have several adaptations that help them to reproduce in the desert.
One such adaptation is the flowers of cactus plants.
The flowers of cacti are often large and showy, and they produce a sweet nectar that attracts pollinators such as bees, hummingbirds, and bats.
The large size of the flowers helps to ensure that pollinators will find the cactus plant and transfer pollen from one cactus flower to another.
This adaptation ensures that cacti can reproduce successfully in the desert.
Another adaptation that helps cacti reproduce in the desert is the production of fruit.
Cactus fruit is often fleshy and colorful, and it contains seeds that animals disperse.
The fleshy fruit attracts animals such as birds and rodents, which eat the fruit and spread the seeds in their droppings.
This ensures that cactus plants can disperse their seeds widely and successfully reproduce in the desert.
How Do Cacti Survive in the Desert Without Water?
Cacti are efficient water users, which helps them survive in the desert.
The leaves of cactus plants are covered with a waxy coating that prevents water loss through evaporation.
Additionally, the stems of cacti are thick and fleshy, which helps to minimize water loss.
Cacti also have shallow roots that help them absorb water quickly when available.
Another adaptation that helps cacti survive in the desert is their ability to store water.
The stems of cacti are filled with spongy tissue that can absorb and store large amounts of water.
This stored water can help the plant to survive during periods of drought.
How Do Cacti Survive in the Desert in Hot Temperatures Without Shade?
Cacti are adapted to survive in hot desert conditions without shade.
Their flattened shape and spines allow them to minimize skin exposure to the sun.
The spines also help to deflect the sun’s heat.
The thick, fleshy stems of cacti store water and help to keep the desert plant cool.
They also have a waxy coating on their skin that helps to reflect sunlight. This helps to keep the plants cool and prevent water loss.
Cacti also have a very low surface area to volume ratio. This helps to minimize the amount of heat absorbed from the sun.
Final Thoughts
Cacti are unique plants that have adapted to survive in the desert.
The adaptations of cacti allow them to store water, minimize water loss, and withstand extreme heat.
These adaptations make cacti well-suited to surviving in the desert environment.
Cacti are a fascinating example of how plants can adapt to their environment in order to survive.
Their adaptations make them well-suited for life in the desert and allow them to thrive in this harsh environment.