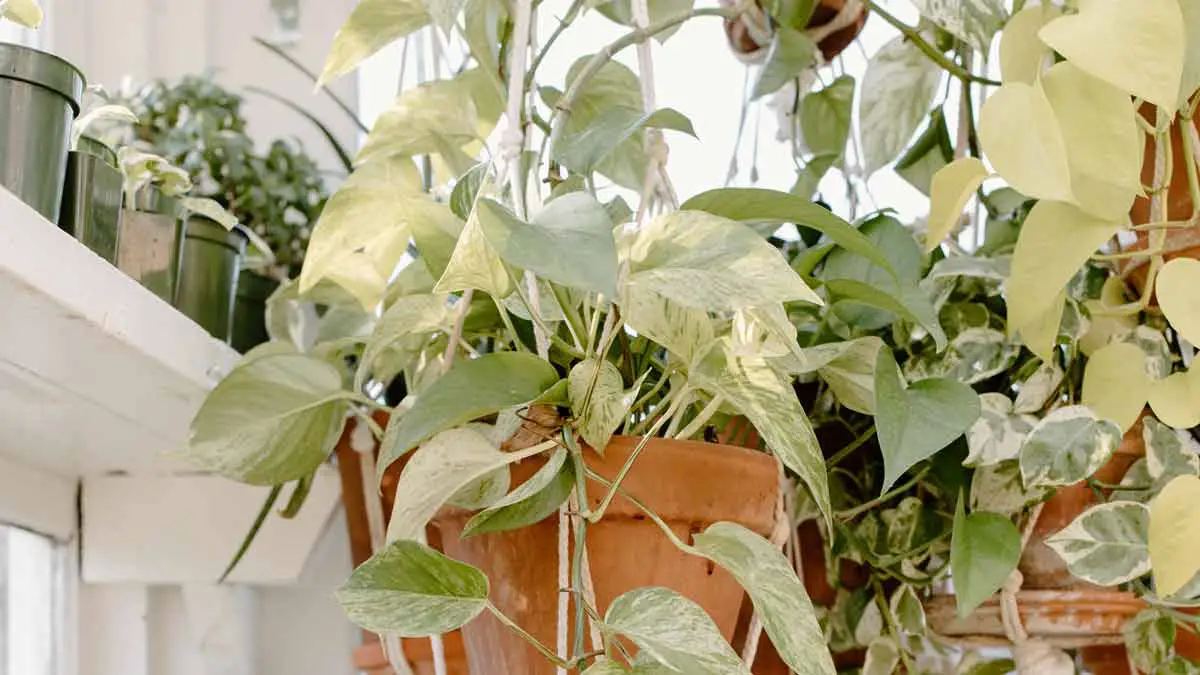
Pothos leaves can turn white due to issues like powdery mildew, sunburn, low light, pests, nutrient deficiency, water quality, or temperature stress. To prevent this, provide proper light, water, and fertilizer. Act promptly to address the specific problem for a healthy, green pothos plant.
Pothos plants are one of the most popular houseplants for their easy care and ability to thrive in various conditions.
But even experienced pothos growers can be stumped when their plant leaves start turning white.
This sudden color change can be alarming, but it’s usually not a cause for concern. In most cases, it’s pretty easy to fix.
Here are seven common reasons why pothos leaves turn white and how to solve the problem.
Why Do Pothos Leaves Turn White?
If you notice your pothos leaves turning white, it’s likely due to one of the following seven reasons.
1. Powdery Mildew
Powdery mildew is a type of fungal disease that affects a wide range of plants, including pothos. It’s characterized by a white, powdery fungus that forms on the leaves and stems of affected plants.
Powdery mildew is most commonly caused by too much moisture or humidity.
If your pothos plant is regularly exposed to humid conditions, it’s more susceptible to this disease.
Too much shade can also contribute to powdery mildew, preventing the leaves from drying out properly.
How To Tell If It’s Powdery Mildew
Powdery mildew usually starts as small, white spots on the leaves of affected plants.
As the disease progresses, the spots will spread and cover the entire leaf surface with a white powder.
The Pothos leaves may also turn brown or yellow, eventually dropping off the plant.
Other signs of powdery mildew include stunted growth and deformed leaves.
How To Treat Powdery Mildew
If you think your pothos plant has powdery mildew, it’s essential to take action immediately. The disease can spread quickly and affect other plants in your home.
To treat powdery mildew, start by pruning off any affected leaves.
Then, increase the ventilation around your plant by opening windows or using a fan. This will help to prevent the disease from spreading.
You can also create a homemade fungicide spray by mixing one tablespoon of baking soda with two and a half tablespoons of horticultural oil in a gallon of water.
Spray the affected leaves with this solution and coat them completely.
Repeat the spray every seven to ten days until the powdery mildew is gone.
2. Sunburn
Pothos plants are native to tropical regions and prefer shaded, humid conditions.
If they’re exposed to too much sun, their leaves can start to turn white. This is because the white leaves are burning from the sun’s rays.
Sunburn is most likely to occur during the summer when the sun is at its strongest.
But even if the weather isn’t particularly warm, your pothos plant can still get sunburned if placed in a spot with direct sunlight.
How To Tell If It’s Sunburn
If your pothos leaves are turning white, and the plant is in a spot where it gets a lot of direct light, it’s likely due to sunburn.
The leaves usually have white patches or streaks on them, and the edges may be brown or crispy.
Sunburned leaves will eventually turn yellow and brown before the plant falls off.
The leaves on the side of the plant facing the sun will be affected first.
How To Treat Sunburn
If you think your pothos plant has sunburn, the best thing to do is move it to a spot with filtered or indirect light.
Pothos plants need bright indirect light to thrive, so a spot near a window should be perfect.
East- or west-facing windows are typically best, as they provide the most indirect light.
You can also try to create more shade for your plant by placing it under a tree or using a sheer curtain.
Just be sure that the spot you choose isn’t too dark, which can cause problems for your pothos plant.
3. Low Light
Pothos plants need bright indirect light to thrive. If they don’t get enough light, their leaves can start to turn white.
Plants need light for photosynthesis, which they use to create food from sunlight.
Without enough light, plants can’t produce the food they need to grow and thrive. This can lead to several problems, including yellowing leaves, stunted growth, and leaf drop.
How To Tell If It’s a Lack Of Light
If your pothos plant is not getting enough light, the leaves will start to turn a pale green or yellow color.
Eventually, the leaves will turn completely white.
Other signs of a lack of light include stunted growth and leaf drop.
If you’re unsure whether your plant is getting enough light, try placing it in a spot where it will get more light for a few days.
If the leaves start to green up, you know that the low light condition was causing the problem.
If the leaves don’t change color, it’s likely due to another issue.
How To Treat a Lack Of Light
If your pothos plant is not getting enough light, try moving it to a spot where it will get more light.
Pothos plants need bright indirect light to thrive, so a spot near a window should be perfect.
An east- or west-facing window is typically best, as it will provide the most indirect light.
You can also try to create more light for your plant by using a grow light.
Grow lights are artificial lights that mimic the sunlight that plants need for photosynthesis.
They’re a great way to provide extra light for plants that aren’t getting enough from natural sources.
4. Pest Infestation
Pests can also cause pothos leaves to turn white. Aphids, mealybugs, and spider mites are all common pests that can infest pothos plants.
These pests suck the sap from the leaves, causing them to turn white.
Aphids are small, pear-shaped, typically black, green, or brown insects. They congregate in large groups on the undersides of leaves and stems.
Mealybugs are small, white insects that look covered in cotton. They tend to congregate in groups on the stems and leaves of plants.
Spider mites are tiny red or brown insects that spin webs on the undersides of leaves. They’re usually found in large numbers on infested plants.
How To Tell If It’s a Pest Infestation
If your pothos plant has a pest infestation, you’ll likely see the pests themselves on the plant.
You may also see stippling or discoloration on the leaves caused by pests sucking the sap from the leaves.
Other signs of a pest infestation include webbing on the leaves and stunted growth.
If you’re unsure whether your plant has a pest infestation, try checking the undersides of the leaves for pests.
You can also place a white sheet of paper under the plant and shake it gently. If there are pests on the plant, they’ll fall onto the paper.
How To Treat a Pest Infestation
If your pothos plant has a pest infestation, you’ll need to treat it as soon as possible.
There are a few different ways to treat pests on plants.
One way is to use an insecticidal soap or neem oil.
These products will kill the pests on contact.
You’ll need to apply them every few days until the pests are gone.
Another way to treat pests is to introduce beneficial insects into your garden.
Beneficial insects, such as ladybugs and lacewings, feed on common garden pests.
This can help to keep the population of pests in check.
You can also try to remove the pests by hand.
This is a good option if you have a small infestation and don’t want to use chemicals on your plant.
To do this, wipe the pests off the leaves with a damp cloth.
You can also place a sticky trap near the plant to trap the pests.
5. Nutrient Deficiency
Nutrient deficiencies can also cause pothos leaves to turn white. The most common nutrient deficiency in pothos plants is a lack of iron.
Iron is essential for producing chlorophyll, which gives leaves their green color.
Without enough iron, the leaves will start to turn yellow. Eventually, they’ll turn completely white.
Other nutrient deficiencies can also cause pothos leaves to turn white. A lack of nitrogen, for example, can cause the leaves to turn pale green or yellow.
A lack of magnesium can cause the leaves to turn yellow or brown.
How To Tell If It’s a Nutrient Deficiency
If your pothos plant has a nutrient deficiency, you’ll likely see yellowing or browning of the leaves.
The leaves may also be smaller than usual and have a distorted shape.
The stems may be weak, and the plant may be stunted.
If you’re unsure whether your plant has a nutrient deficiency, you can take a sample of the soil to a garden center or nursery and have it tested.
Soil tests will tell you what nutrients are present in the soil and how much of each one there is.
How To Treat a Nutrient Deficiency
If your pothos plant has a nutrient deficiency, you’ll need to fertilize it.
You can use a specially formulated fertilizer for pothos plants or a general-purpose fertilizer.
Apply the fertilizer according to the directions on the package.
You should also consider amending the soil with compost or other organic matter.
This will help improve the soil’s quality and increase its ability to hold nutrients.
6. Water Quality
The quality of the water you use to water your pothos plant can also affect its leaves.
If the water is too high in salt, it can cause the leaves to turn white. This is because salt interferes with the plant’s ability to absorb water and nutrients.
Chlorine and other chemicals in tap water can also cause the leaves to turn white. These chemicals can damage the plant’s cells and prevent them from absorbing water and nutrients.
How To Tell If It’s Water Quality
If the quality of the water you’re using to water your pothos plant is causing the leaves to turn white, you’ll likely see other symptoms as well.
The leaves may be shriveled and dry, and the plant may be wilting.
It’s also expected that the soil will be white or salt-encrusted.
If you’re unsure whether the water you’re using is causing the problem, try watering your plant with distilled water or rainwater.
If the leaves start to green up within a few days, you know that the water quality was the issue.
How To Treat Water Quality Issues
If the water you’re using to water your pothos plant is high in salt or chlorine, you’ll need to find an alternative water source.
You can use distilled water, rainwater, or water that’s been left out for 24 hours to allow the chemicals to evaporate.
You should also flush the soil with clean water to remove any build-up of salt or chemicals.
7. Temperature Stress
Temperature stress is another common cause of pothos leaves turning white.
Pothos plants prefer temperatures between 60 and 75 degrees Fahrenheit. However, they can tolerate temperatures as low as 50 and as high as 90 degrees.
If the temperature gets too hot or too cold, it can cause the leaves to turn white.
Fluctuations in temperature can also cause the leaves to turn white.
How To Tell If It’s Temperature Stress
If the temperature is too hot or cold, you’ll likely see other symptoms besides the plant leaves turning white.
The leaves may be wilted, and the plant may be stunted.
If the temperature fluctuates frequently, you may see yellow or brown spots on the leaves. These spots are called “leaf scorch.”
How To Treat Temperature Stress
If the temperature is too hot or cold, you’ll need to move your plant to a more temperature-neutral location.
You can also try using a grow light to provide additional warmth or a fan to provide additional cooling.
If the temperature fluctuates frequently, you’ll need to take steps to stabilize the temperature.
This may involve moving the plant to a location less exposed to temperature changes or using a grow light with a built-in thermostat.
How To Prevent Pothos Leaves From Turning White
The best way to prevent your pothos leaves from turning white is to give them the right amount of light, water, and fertilizer.
Pothos plants do best in bright indirect sunlight.
If you notice that your plant’s leaves are turning white, it could be a sign that it’s not getting enough light or that the sunlight is too direct.
To prevent this, move your plant to where it will get bright indirect sunlight.
You should also make sure to water your pothos plant when the soil is dry to the touch.
If you notice that the leaves are wilting or turning yellow, that’s a sign that you need to water it more often.
Finally, you should fertilize your pothos plant once a month with a balanced fertilizer.
It’s also recommended to repot your pothos plant every year or two to ensure fresh soil.
If you follow these care tips, you should be able to prevent your pothos leaves from turning white.
Final Thoughts
Pothos plants are one of the most popular houseplants because they’re easy to care for and look beautiful.
But even with the best care, your pothos leaves may turn white.
If you notice your pothos leaves turning white, it’s essential to take action quickly.
Many of the causes of white leaves are easily remedied, but if left untreated, they can lead to significant problems for your plant.
So, keep an eye on your pothos leaves, and if you see any hint of white, use the tips in this article to figure out the cause and take action accordingly.
With some care, you can get your pothos plant to look healthy and green again in no time!